- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Permitting_Telnet_access_to_Catalyst_Switches
Lab Objective:
The objective of this lab exercise is for you to learn and understand how to configure a switch to be accessed remotely via Telnet. By default, you can telnet to a switch but cannot log in if no password has been set.
Lab Purpose:
Telnet access configuration is a fundamental skill. More often than not, switches are accessed and configured remotely via Telnet. As a Cisco engineer, as well as in the Cisco CCNA exam, you will be expected to know how to configure a switch to allow an administrator to log in via Telnet.
Certification Level:
This lab is suitable for both CCENT and CCNA certification exam preparation.
Lab Difficulty:
This lab has a difficulty rating of 4/10.
Readiness Assessment:
When you are ready for your certification exam, you should complete this lab in no more than 10 minutes.
Lab Topology:
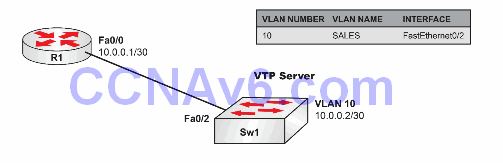
Please use the following topology to complete this lab exercise:
Task 1:
Configure hostnames on Sw1 and R1 as illustrated in the topology.
Task 2:
Create VLAN10 on Sw1 and assign port FastEthernet0/2 to this VLAN as an access port.
Task 3:
Configure IP address 10.0.0.1/30 on R1’s FastEthernet0/0 interface and IP address 10.0.0.2/30 on Sw1’s VLAN10 interface. Verify that R1 can ping Sw1, and vice versa.
Task 4:
Configure Telnet access to Sw1 using the password CISCO. The password is case-sensitive so take that into consideration in your configuration. Verify your configuration by creating a Telnet session from R1.
Configuration and Verification
Task 1:
For reference information on configuring hostnames, please refer to earlier labs.
Task 2:
For reference information on configuring and verifying VLANs, please refer to earlier labs.
Task 3:
For reference information on configuring IP interfaces and SVIs, please refer to earlier labs.
Task 4:
Sw1#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL/Z. Sw1(config)#line vty 0 15 Sw1(config-line)#password CISCO Sw1(config-line)#login Sw1(config-line)#end Sw1#
NOTE: Most people forget the fact that switches typically have 16 VTY lines (numbered 0 to 15), unlike routers, which typically have five VTY lines (numbered 0 to 4). Take care to remember this when configuring switches, as you may leave some lines unsecured if you use line vty 0 on a router. We have already discussed that GNS3 has more VTY lines.
R1#telnet 10.0.0.2 Trying 10.0.0.2 ... Open User Access Verification Password: Sw1# Sw1#
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment